There is no doubt that a woman’s hair is a key element of her beauty. Therefore, hair loss is considered one of the most distressing problems women face. For this reason, hair transplantation for women—and the advances in this procedure—has become an important topic of interest to many. Follow along with this article to learn everything about hair transplant for women, including its types, procedure, complications, and results.
Causes of Hair Loss in Women
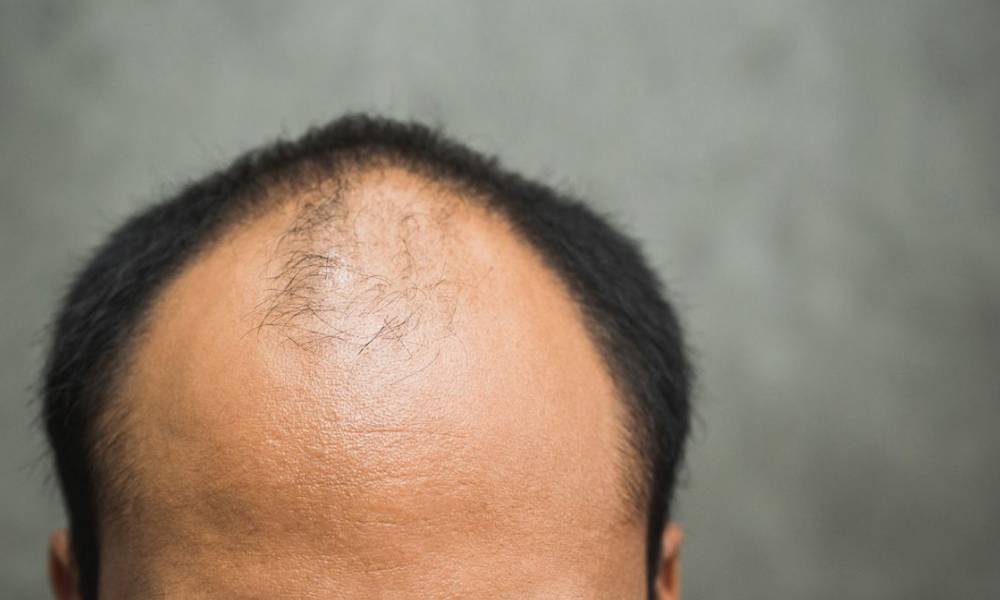
The most common cause of hair loss in women is female pattern baldness, also known as androgenetic alopecia. Other possible causes include:
- Genetic predisposition to hair loss
- Autoimmune diseases
- Hormonal changes
- Certain medications
- Menopause
- Pregnancy
- Excessive stress
- Rapid weight loss
- Iron deficiency
What Is Hair Transplant for Women?
A female hair transplant is a procedure in which a cosmetic surgeon transplants hair to bald or thinning areas of the scalp. Typically, the surgeon transfers hair from the sides or back of the head to the front or crown. The procedure is usually performed in a medical clinic under local anesthesia.
Types of Hair Transplant Procedures for Women
There are two main methods used in female hair transplantation:
- Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
- The surgeon removes a strip of scalp, usually from the back of the head.
- The donor area is then closed with sutures.
- The scalp strip is divided into smaller grafts using a scalpel.
- Tiny incisions are made in the recipient area using a needle or blade.
- The surgeon implants hair grafts into these incisions.
- The surgical sites are covered with gauze or a dressing.
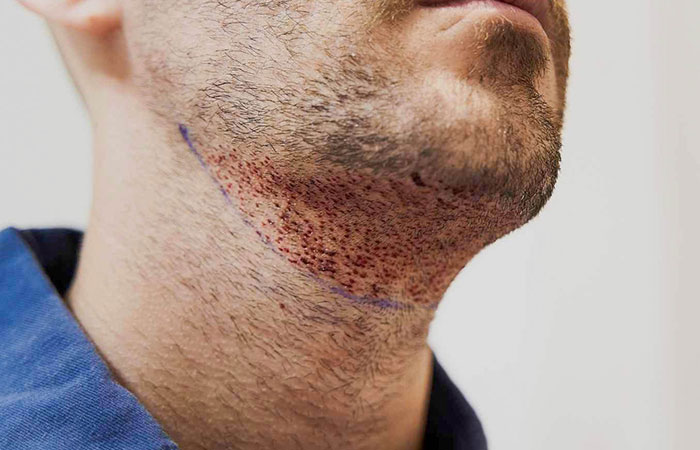
- Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
- In FUE, the surgeon extracts individual hair follicles directly from the donor area.
- Small incisions are made in the recipient area, and each follicle is transplanted into these sites.
- The treated area is covered with a bandage.
Eligibility Criteria for Hair Transplant in Women
Hair transplantation is suitable for women who:
- Experience permanent hair loss or noticeable thinning in specific areas
- Have a healthy donor area (typically the back of the scalp)
- Are in good health and free from medical conditions that contraindicate surgery
- Have realistic expectations about the results
- Are preferably over 25 years old, when hair loss patterns become more stable
Who Is Not a Candidate for Hair Transplantation?
- Women with temporary hair loss that can be treated medically
- Those with active scalp diseases (e.g., eczema, psoriasis)
- Women with insufficient donor follicles
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women, as hormonal changes can affect outcomes
Preoperative Preparations
- Stop smoking at least 24 hours before surgery, as it can delay wound healing.
- Avoid alcohol for three days before the procedure.
- Do not cut your hair prior to surgery; the donor area should be left untouched.
- Massage the scalp daily for 10 minutes for 2–4 weeks before surgery to improve blood circulation and skin elasticity.
- Undergo blood tests, and if over 45 years old, possibly an ECG.
- Discontinue aspirin or anti-inflammatory medications two weeks before surgery.
- Avoid antidepressants and blood thinners for two weeks before surgery.
- Stop taking supplements and multivitamins two weeks prior.
Procedure Steps
- The donor area is cleaned and numbed using local anesthesia.
- After extracting grafts, the surgeon makes tiny incisions in the recipient area.
- Each graft, containing 1–3 hairs, is carefully implanted.
- Up to 2,000 grafts can be transplanted in a single session.
- The surgery usually takes 5–8 hours.
Recovery After Hair Transplantation
- You will need to wear bandages for one to two days.
- The doctor may prescribe antibiotics and anti-inflammatory medications.
- The donor area typically heals in 7–10 days.
- Scalp crusting may occur for 6–7 days post-procedure.
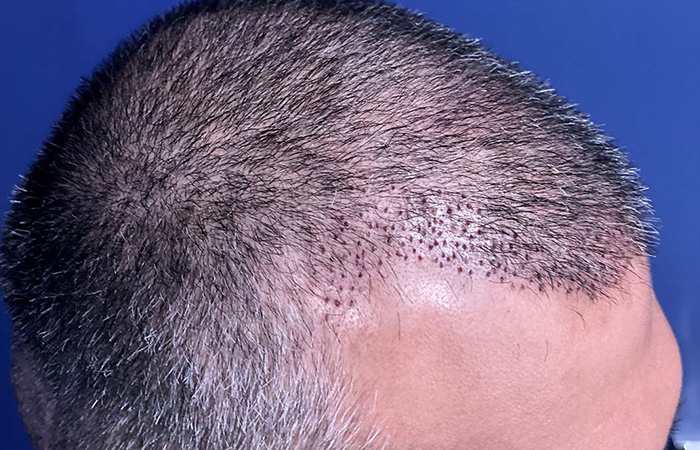
Results of Hair Transplantation for Women
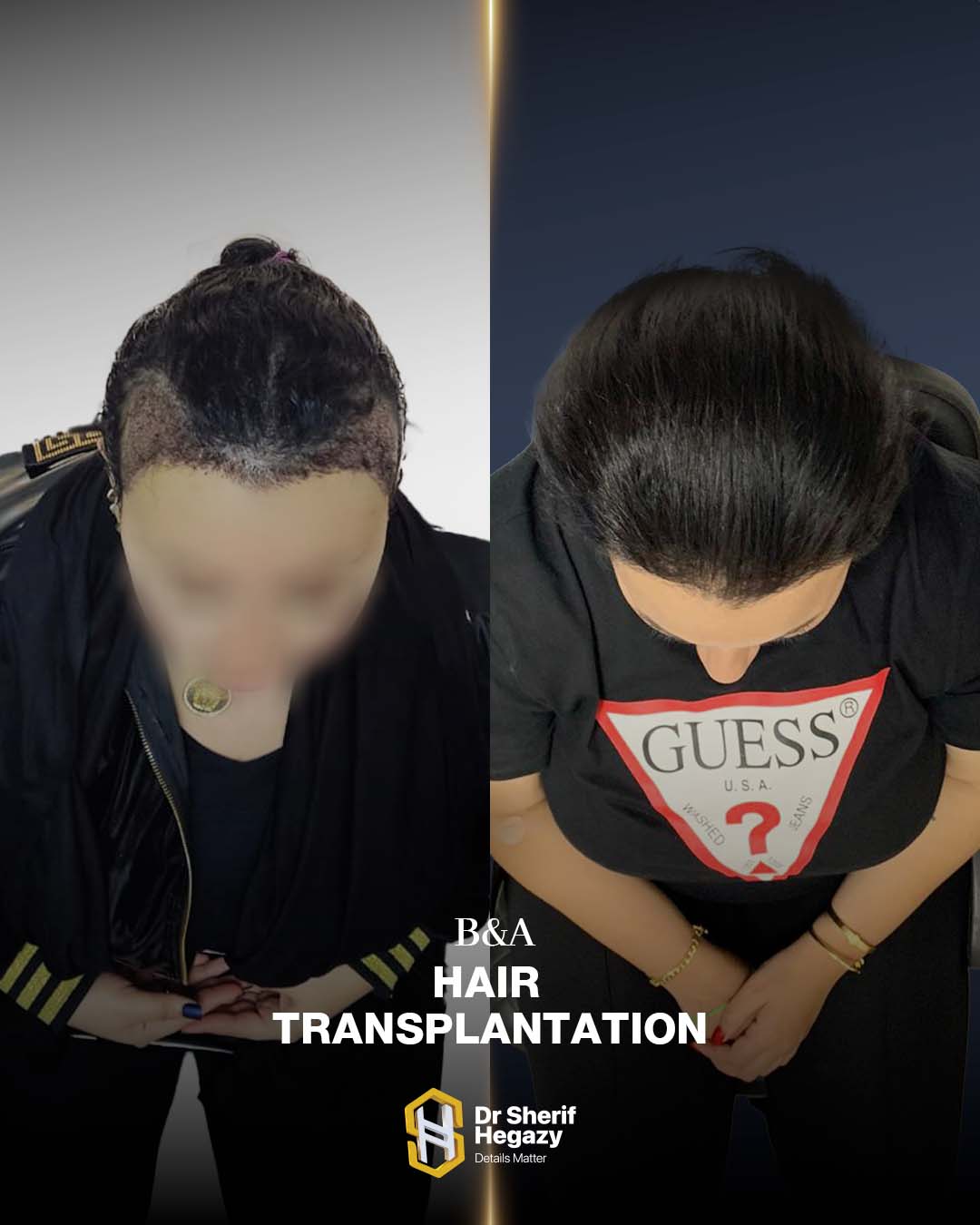

- The transplanted hair will fall out within 2–3 weeks after the procedure.
- New hair growth begins after 3–4 months and continues for life.
- Noticeable results appear between 6–10 months, with about 90% of the outcome visible after one year.
Postoperative Care Tips
- Wash your hair gently for the first five days.
- Use mild shampoo and avoid harsh hair products.
- Protect your scalp from sunlight during the first few days.
- Avoid combing or brushing the treated areas for three weeks.
- Resume physical exercise after 5–7 days.
Cost of Hair Transplant for Women
- The cost depends on the treatment area, the number of grafts, the surgeon, and the chosen technique.
- In Egypt, the price ranges from $1,500 to $4,000.
- In other Arab countries, it ranges between $1,500 and $8,000 on average.
Possible Complications
Most side effects are mild and temporary, including:
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Swelling of the scalp
- Bruising around the eyes
- Itching
- Folliculitis (inflammation of hair follicles)
- Numbness or reduced sensation in the treated areas
Alternatives to Hair Transplantation
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP): Injections of platelet-rich plasma derived from your blood to stimulate hair growth, repeated every six months.
- Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): At-home use of laser devices to stimulate follicles.
- Scalp Micropigmentation (SMP): Tattooing tiny dots on the scalp to create the illusion of density.
- Propecia (Finasteride): A medication that may be prescribed post-menopause, with visible results after about three months.
- Minoxidil: A topical treatment that stimulates growth; results stop if discontinued.
Always consult your physician before starting any of these treatments.
Differences Between Female and Male Hair Transplants
- Pattern of Hair Loss: Men typically experience baldness at the hairline or crown, while women have diffuse thinning, especially on the top of the scalp.
- Target Area: Women often seek to improve overall density or refine the hairline or eyebrows; men aim to restore large bald patches.
- Donor Area Preparation: Women rarely require full shaving, particularly with techniques like DHI, to maintain aesthetics.
- Aesthetic Goals: Women prioritize natural appearance and precise follicle placement, while men often focus on coverage.
- Hormonal Factors: Female hair loss is often linked to hormonal changes (e.g., pregnancy, menopause), requiring careful evaluation.
- Psychological Impact: Hair loss tends to have a stronger emotional impact on women, making psychological support important.