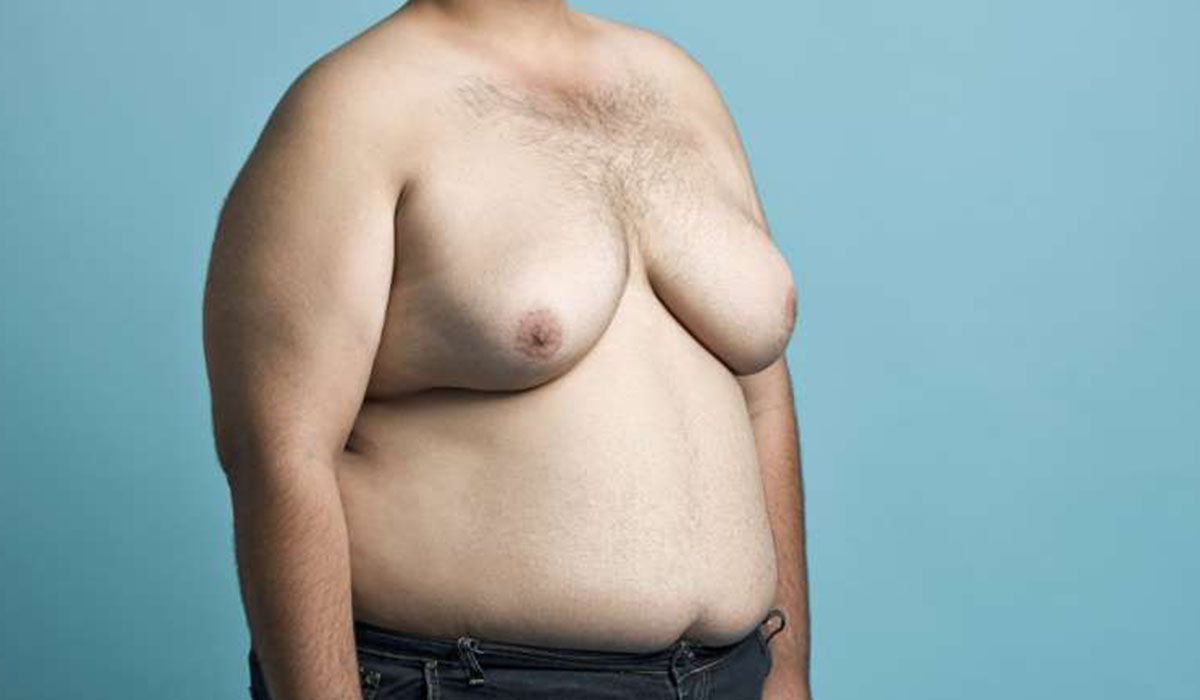
Gynecomastia in men, also known as breast enlargement, is a common medical condition that affects males of all ages—from infants to the elderly. It is characterized by the enlargement of breast tissue, leading to a breast-like appearance similar to that of females. According to the American Endocrine Society, approximately 30–60% of men experience gynecomastia at some point in their lives. While it is often not a health threat, it can cause psychological embarrassment or physical discomfort. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, treatment options, cases requiring surgical intervention, and prevention tips for gynecomastia.
What is Gynecomastia in Men?
Gynecomastia is the enlargement of male breast tissue caused by an imbalance between estrogen and testosterone hormones. Estrogen, the female hormone, stimulates breast tissue growth, whereas testosterone, the male hormone, limits it. When estrogen levels rise or testosterone levels fall, gynecomastia may occur. It can affect one or both breasts and may be asymmetrical in size.
Symptoms of Gynecomastia in Men
The main symptoms include:
- Swelling of breast tissue: May occur in one or both breasts and is often asymmetrical.
- Breast pain or tenderness: Particularly common in adolescents.
- Nipple sensitivity: Especially with contact from clothing.
- Nipple discharge: Rare, but may be clear or milky.
When to See a Doctor
Consult a doctor if you notice:
- Persistent swelling lasting more than 6 months.
- Severe pain or ongoing tenderness.
- Nipple discharge.
- Hard lumps or changes in skin texture.
- A family history of breast cancer.
Grades of Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia is classified into four grades based on severity, which helps determine the appropriate treatment:
- Grade I: Mild enlargement around the nipple without skin sagging or significant breast size increase.
- Grade II: Enlargement extending to the areola, with slight size increase and no skin sagging.
- Grade III: Noticeable enlargement with mild skin sagging.
- Grade IV: Severe enlargement with significant skin sagging, resembling a female breast.
Causes of Gynecomastia
This condition may arise from multiple factors, including:
Natural Hormonal Changes
- Infants: Over 50% of male infants develop gynecomastia due to maternal hormones; it usually resolves within a few weeks.
- Adolescents: Common during puberty (affecting 40% of boys aged 14–15.5 years) due to hormonal changes; typically resolves within 6 months to 2 years.
- Older Adults: Affects 24–65% of men aged 50–80 due to declining testosterone levels, particularly in those with obesity.
Medications
Certain drugs may influence hormone balance and cause gynecomastia, including:
- Anti-androgens (e.g., flutamide, finasteride, spironolactone).
- Anabolic steroids.
- Antivirals (e.g., efavirenz).
- Tricyclic antidepressants.
- Antibiotics.
- Opioid painkillers.
- Ulcer medications (e.g., cimetidine, omeprazole).
- Chemotherapy.
- Heart medications (e.g., digoxin).
- Metoclopramide.
Substance Abuse
Use of the following substances can lead to gynecomastia:
- Alcohol.
- Anabolic steroids.
- Amphetamines.
- Cannabis.
- Heroin.
- Methadone.
Health Conditions
Some illnesses affect hormone balance or directly cause gynecomastia, such as:
- Hypogonadism (e.g., Klinefelter syndrome or pituitary failure).
- Tumors (in the testicles, adrenal glands, or pituitary gland).
- Hyperthyroidism.
- Kidney failure (affecting 50% of dialysis patients).
- Liver failure or cirrhosis.
- Malnutrition.
Herbal Products
Some products, like tea tree oil and lavender oil, may mimic estrogen or suppress testosterone, contributing to gynecomastia.
Diagnosis of Gynecomastia in men
Diagnosis typically involves:
- Physical exam: To assess the size and feel of breast tissue.
- Medical history: To identify related medications or health conditions.
- Tests, which may include:
- Blood tests to measure hormone levels.
- Breast ultrasound imaging.
- Mammogram to rule out breast cancer.
- Biopsy (in rare cases) for microscopic examination.
Treatment of Gynecomastia
In many cases, gynecomastia resolves on its own, especially in infants and adolescents. If persistent, treatment options include:
- Observation: Often sufficient for mild cases.
- Medications: Such as tamoxifen or estrogen blockers; a doctor’s evaluation is required to weigh benefits and risks.
- Surgery: Used in severe cases or when gynecomastia causes psychological distress.
Know more about gynecomastia non-surgical treatment
Gynecomastia Surgery
Many men prefer surgery for cosmetic or psychological reasons. Options include:
- Liposuction: Removes excess fat, suitable for pseudo gynecomastia due to fat buildup.
- Gland excision: Removes enlarged glandular tissue through a small incision around the nipple.
- Combination surgery: In advanced cases, both liposuction and gland excision may be used, sometimes with skin removal.
- Surgery is usually performed under general anesthesia, and scars typically fade over time. For more details, refer to the American Society of Plastic Surgeons.
Prevention of Gynecomasta
Although it may be difficult to prevent in some cases, risks can be reduced by following these tips:
- Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity increases gynecomastia risk.
- Avoid alcohol and drugs: Such as cannabis, heroin, and steroids.
- Review medications: Consult your doctor about drugs that may cause gynecomastia.
- Exercise regularly: Chest exercises, like weightlifting, may help improve chest appearance.
- Manage underlying health conditions: Such as liver or kidney disease to maintain hormonal balance.
Conclusion
Gynecomastia in men is a common condition that may be embarrassing but is usually not serious. It can result from natural hormonal changes, medications, or medical conditions. If you experience symptoms of gynecomastia, consulting a specialist is the first step in determining the cause and selecting the appropriate treatment, whether observation, medication, or surgery. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, you can reduce your risk and maintain self-confidence.