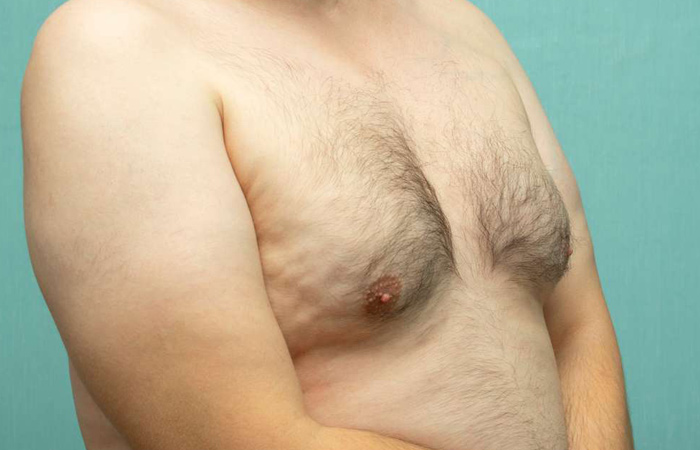
Gynecomastia surgery in men, also known as male breast reduction or “Gyno surgery” is an effective solution for addressing enlarged breast tissue—a condition that may impact self-esteem or cause physical discomfort. These surgical procedures aim to remove excess fat, glandular tissue, and sometimes skin, to achieve a more masculine and symmetrical chest appearance. Thanks to modern techniques, gynecomastia surgery is now safe, has a quick recovery time, and offers long-lasting results. In this article, we review the types of gynecomastia surgery, how they are performed, preparation, recovery, risks, and expected outcomes.
Types of Gynecomastia Surgery
The surgical approach varies depending on the type of gynecomastia and the severity of the condition. The surgeon selects the most appropriate technique after evaluating the patient’s case. The main types include:
Male Breast Liposuction
- Description: A small incision is made, typically around the nipple or under the armpit, and a thin tube (cannula) connected to a suction device is inserted to remove excess fat. Advanced methods such as ultrasound-assisted liposuction are used for enhanced precision.
- Indication: Ideal for cases where the enlargement is mainly due to fat accumulation (pseudo-gynecomastia), with minimal glandular tissue.
- Advantages: Small incisions, minimal scarring, and quick recovery.
Glandular Tissue Excision
- Description: The surgeon makes an incision around the areola or elsewhere to remove excess glandular tissue. Endoscopic tools may be used to minimize the size of the incisions.
- Indication: Necessary when the enlargement is due to increased glandular tissue (true gynecomastia).
- Advantages: Effective for removing firm tissue that cannot be eliminated through liposuction.
Combination of Liposuction and Excision
- Description: The surgeon combines liposuction and tissue excision to remove both fat and glandular tissue in a single procedure.
- Indication: Used in mixed cases involving both tissue types, which are most common.
- Advantages: Comprehensive results with significant improvement in chest contour.
Excess Skin Removal or Tightening
- Description: In severe cases, the surgeon removes or reshapes excess skin to prevent sagging after tissue removal. This may include repositioning the nipple for a more natural appearance.
- Indication: Necessary when significant skin sagging is present, especially in advanced grades of gynecomastia.
- Advantages: Improves chest appearance in severe cases.
Preoperative Preparation
Before undergoing gynecomastia surgery, patients should:
- Undergo medical testing: Including blood tests to confirm overall health.
- Adjust medications: Discontinue blood-thinning drugs like aspirin or NSAIDs as advised by the physician.
- Quit smoking: To enhance healing and reduce complications.
- Discuss expectations: With the surgeon to set realistic goals and choose the best technique.
- Fasting: Usually required for 6–8 hours before surgery if general anesthesia is used.
Gynecomastia Surgical Steps
Gynecomastia surgery is typically an outpatient procedure, meaning patients return home the same day. Steps include:
- Anesthesia: General anesthesia is commonly used for patient comfort; local anesthesia may be used in minor cases.
- Incisions: Small incisions are made around the areola or under the armpit, depending on the technique.
- Tissue removal: Fat is removed through liposuction, glandular tissue via excision, and excess skin if needed.
- Closing incisions: Sutures are used to close incisions, and drainage tubes may be placed to prevent fluid buildup.
- Duration: The surgery takes 1 to 2 hours, depending on the complexity.
Advanced techniques like endoscopy and ultrasound-assisted liposuction help reduce scarring and improve results.
Gynecomastia Postoperative Recovery
After surgery, patients must follow specific guidelines for proper healing:
- First few days: Wear a compression garment or bandage for 1–2 weeks to reduce swelling and bleeding.
- Pain management: Take prescribed pain medications and avoid drugs that may increase bleeding.
- Return to activities: Resume work in 3–7 days if it’s non-physical. Avoid intense exercise or lifting for 4–6 weeks.
- Follow-up: Attend regular doctor visits to monitor healing and remove sutures or drainage tubes if applicable.
- Final results: Typically visible within 3–6 months as swelling subsides and the chest contour stabilizes.
Risks and Complications
Although gynecomastia surgery is generally safe, potential risks include:
- Bleeding or hematoma: May occur within the first few days.
- Infection: Rare but possible if hygiene instructions aren’t followed.
- Scarring: Minimal due to small incisions, and advanced techniques help reduce visibility.
- Nipple sensitivity loss: May be temporary or permanent in rare cases.
- Asymmetry: Minor differences between the breasts may occur.
- Fluid buildup: Can be prevented with drainage tubes.
Choosing an experienced surgeon and adhering to post-operative care greatly reduces these risks.
Results of Gynecomastia Surgery
Gynecomastia surgery offers satisfying outcomes, including:
- More masculine chest: Reduced breast size and improved contour.
- Boosted self-confidence: Relief from psychological embarrassment.
- Physical comfort: Less pain or nipple sensitivity when wearing clothes.
- Lasting results: Provided a healthy weight is maintained and contributing factors are avoided.
- These procedures have high satisfaction rates and significantly enhance quality of life.
Conclusion
Gynecomastia surgery is a safe and effective option for treating persistent male breast enlargement, whether caused by fat, glandular tissue, or both. With techniques like liposuction and tissue excision, excellent cosmetic results can be achieved with fast recovery and minimal scarring. If you’re considering gynecomastia surgery, consulting a board-certified plastic surgeon is the first step in determining the best solution for your case. By following medical advice, you can restore a balanced chest appearance and enjoy greater self-assurance.